A brief history of Fibre Optics
- Cloud networking
- November 8, 2013
- RSS Feed
Explore the fascinating history of fibre optics, from its ancient origins with the Romans drawing glass fibres in 27BC to its modern-day applications in telecommunications, medicine, and entertainment. Discover how this ubiquitous technology evolved from a simple concept into a cornerstone of connectivity.
While fibre technology has become ubiquitous in today’s modern telecommunications networks, did you know that fibre optic technology has been around for a very long time and is quite simple in concept. Glass dates back to around 3000BC and the Romans were drawing glass into fibre as early as 27BC. So while fibre has become an everyday technology ranging from medical to telecommunications to entertainment applications, you can see from its history that fibre has come a very long way in a very short time.
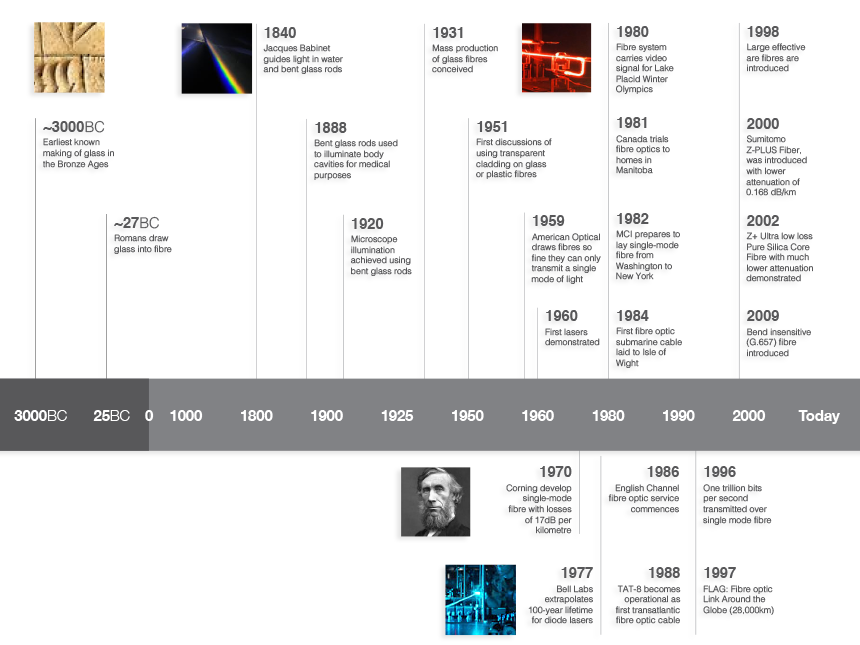
The following is an historical chronology of some of the key milestones with regards to fibre optics.
~3000BC - Earliest known making of glass in the Bronze Ages.
~27BC - Romans draw glass into fibre.
1840s - Jacques Babinet guides light in water and bent glass rods.
1888 - Bent glass rods used to illuminate body cavities for medical purposes.
1920s - Microscope illumination achieved using bent glass rods.
1931 - Mass production of glass fibres conceived.
1951 - First discussions of using transparent cladding on glass or plastic fibres.
1959 - American Optical draws fibres so fine they can only transmit a single mode of light.
1960 - First lasers demonstrated.
1966 - Charles Kao indicates that fibre losses could be reduced to below 20dB per kilometre for office to office communications.
1967 - Corning starts making high-loss fibres. Research into sing titanium doping and silica cladding commences.
1970 - Corning develop single-mode fibre with losses of 17dB per kilometre by using titanium doping. Also first room-temperature, continuous-wave semiconductor lasers made.
1971 - Bell Labs, University of Southampton and CSIRO in Australia experiment with liquid-core fibres.
1973 - Diode laser lifetime reaches 1000 hours.
1975 - First non-experimental fibre optic link installed by Dorset police.
1976 - First fibres manufactured with low loss of 0.47 dB per kilometre. Lifetime of lasers reaches 100,000 hours (10 years).
1977 - Bell Labs extrapolates 100-year lifetime for diode lasers.
1978 - First Fibre Optic Con trade show held in Boston.
1980 - Fibre system carries video signal for Lake Placid Winter Olympics. 9.5km submarine cable lay in Loch Fyne.
1981 - Canada trials fibre optics to homes in Manitoba.
1982 - MCI prepares to lay single-mode fibre from Washington to New York.
1984 - First fibre optic submarine cable laid to Isle of Wight by BT.
1986 - English Channel fibre optic service commences.
1988 - TAT-8 becomes operational as first transatlantic fibre optic cable.
1996 - One trillion bits per second transmitted over single mode fibre.
1997 - FLAG (fibre optic link around the globe) went into service spanning over 28,000kms and offering 10Gbps services.
1998 - Large effective are fibres are introduced.
2000 - Sumitomo Z-PLUS Fiber, was introduced with lower attenuation of 0.168 dB/km
2002 - Z+ Ultra low loss Pure Silica Core Fibre with much lower attenuation was demonstrated in 2002
2006 - Ribbon fibre cable is introduced to increase fibre core counts in smaller diameter cables.
2009 - Bend insensitive (G.657) fibre introduced.